The Green Rush
The global cannabis industry has seen significant growth, fuelled by changing regulations, shifting public perceptions, and increasing demand for both medicinal and recreational cannabis. According to Statista, the cannabis market is forecasted to reach US$68.47Bn in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2.33%, potentially reaching over $75.09 bn by 2029. But these figures can’t be accurate because the cannabis industry runs of various factors like macroeconomic factors, regulations, customer preferences, etc. The medicinal cannabis sector is expanding due to broader acceptance and its use in treating various conditions, while recreational cannabis is growing rapidly, especially in regions with progressive policies like the U.S. and Canada. The CBD market is also growing fast, and is expected to grow at a CAGR of ~15.8% from 2024 to 2030.
Geographical Distribution:
- North America: The U.S. is the largest cannabis market, with states like California, Colorado, and Oregon leading in both medicinal and recreational sales. Despite federal prohibition, state-level legalization is expanding, and full legalization could save the U.S. an estimated $3.6 billion spent annually on federal law enforcement. Canada is one of the countries to fully legalize recreational cannabis in 2018.
- Europe: Several countries like Germany, Italy, and the UK have legalized medicinal cannabis, with Germany being the largest market in Europe. Recreational cannabis remains illegal, but support for legalization is growing, especially in the Netherlands, known for its liberal policies and cannabis coffee shops.
- Latin America: Uruguay fully legalized recreational cannabis, and Mexico is legal for both recreational (June 2021) and medicinal purposes. Brazil permits medicinal cannabis, focusing on CBD treatments for certain conditions.
- Asia-Pacific: Australia has legalized medicinal cannabis, with growing markets in states like New South Wales. Thailand legalized medicinal cannabis in 2018, becoming the first Southeast Asian country to do so. Most Asian countries, including South Korea, allow cannabis for medical use only.
- Africa: South Africa decriminalized private cannabis use in 2018, and its medicinal cannabis sector is expanding. Cannabis remains illegal in most African countries, but there is increasing interest in its economic potential, particularly in medicinal use and hemp cultivation.
Growth Drivers
The rapid growth of the cannabis industry can be attributed to several key drivers. Legalization plays a central role by generating tax revenue, boosting job creation, and increasing access to regulated products. This trend supports both the medicinal and recreational cannabis markets. Cannabis legalization has led to significant tax revenue, particularly in places like California, where cannabis taxes contribute millions to the state economy, helping to fund essential public services.
Economic growth also drives cannabis market expansion. Countries with higher GDPs tend and legalized cannabis, to have more disposable income, which increases investments for cannabis products, particularly as a more affordable alternative to other expensive pharmaceuticals or alcohol. The growing shift in social attitudes toward cannabis has also fuelled its growth, with increasing acceptance across demographics. People are now more aware of cannabis' medicinal and recreational benefits, reducing the stigma once associated with its use.
The medical cannabis sector is another key driver. With ongoing research showing cannabis’ effectiveness in treating various health conditions, demand for medical cannabis products continues to rise. Conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and cancer-related symptoms are commonly treated with cannabis. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly involved in the development of cannabis-based medications, such as Epidiolex (a CBD-based drug) and Sativex (a THC and CBD spray), both FDA-approved for specific conditions. As more doctors prescribe cannabis for therapeutic use, its integration into medical care increases.
Cannabis accessibility has also expanded, with retail chains, e-commerce platforms, and other specialized services helping to meet demand. Because delivery of cannabis was popular even before legalization, thus it plays an important role in the culture. Additionally, patients dealing with sensitive medical problems prefer to consume cannabis privately. Delivery cannabis services offer a discreet and confidential method of obtaining their medication, thereby minimizing the potential stigma associated with visiting a public dispensary.
According to Forbes; Chris Vaughn, the CEO of Pacific Consolidated Holdings, says,
“In cannabis, delivery is how people have shopped forever. The dispensary is the new, unusual shopping behaviour.”, “Delivery is how people buy weed.”
Legalization in more regions allows people in previously restricted areas to access safe, regulated cannabis products. Additionally, while inflation impacts consumer spending, the cannabis industry remains somewhat insulated. Consumers continue to purchase cannabis, particularly medical cannabis, which is seen as a more affordable alternative to traditional medications and recreational drugs during economic downturns.
Industrial Hemp Revolution
Industrial hemp, a cannabis variety with low THC (below 0.3%), is used for textiles, plastics, biofuels, construction materials, food, and cosmetics. It’s an eco-friendly crop, requiring fewer pesticides and water compared to conventional crops like cotton. Hemp also helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by absorbing carbon dioxide effectively.
Hemp products include:
- Textiles & Clothing: Hemp fibres are strong and durable, making them ideal for textiles, ropes, and sustainable fashion alternatives to cotton.
- Construction Materials: Hemp-based products like hempcrete (a lightweight concrete alternative) and insulation are used in sustainable building. Studies show hemp composites offer better insulation than traditional materials.
- Food & Nutraceuticals: Hemp seeds contain protein, vitamins, minerals and polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly omega-3 fatty acids. Hemp oil is used in foods, supplements, and cosmetics.
- Biodegradable Plastics & Paper: Hemp is also used to create eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based plastics and paper products.
The Dark-side of Cannabis Market
Despite increasing legalization, the illegal cannabis market remains a significant issue globally. Legal cannabis incurs costs like licensing, taxes, and regulatory compliance, which illegal sellers avoid. As a result, illegal market continues to thrive, particularly in regions where cannabis remains illegal or unregulated. In the U.S., the illegal cannabis market is still estimated to be larger than the legal one in many areas.
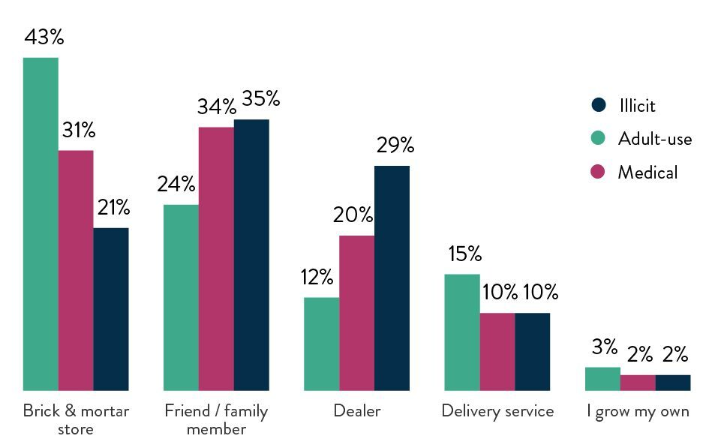
(Source: New Frontier Data 2020; Consumer Survey; US General Population)
The illegal market spans countries where cannabis is entirely prohibited, such as parts of Asia and the Middle East, to those with partial or full legalization like the U.S. and Europe. Cannabis is often grown in unauthorized sites, ranging from small domestic grows to large illegal operations, some located in remote areas to evade law enforcement. International smuggling remains widespread, with illicit trade routes running through countries with strict anti-drug laws.
Transactions in the illegal market often occur through illicit dealers or encrypted platforms, such as darknet markets. In many areas, especially where cannabis is prohibited, it is sold in unregulated environments, often through illicit dealers or underground networks. The illegal market operates without regulation, meaning there are no quality control standards or safety checks. This can lead to products being contaminated with harmful pesticides, Mold, or even dangerous synthetic substances. Prices in the illegal market are inconsistent, influenced by factors like demand, availability, and risk. This leads to crime, violence, and organized criminal activity. Governments lose potential tax revenue, and public health risks increase as consumers may unknowingly purchase unsafe products.
Cannabis Tourism
Cannabis tourism is a rapidly growing segment within the global tourism industry, attracting travellers to destinations where cannabis use is legal for medicinal or recreational purposes. This type of tourism allows visitors to experience cannabis culture, consume cannabis, explore cultivation, attend cannabis events, and more.
Popular Cannabis Tourism Destinations
- Europe: The Netherlands, especially Amsterdam, is famous for its toleration policy that allows for the sale of cannabis in cannabis-friendly coffeeshops, offering on-site consumption and cannabis tours. Spain, while having strict recreational laws, is growing as a destination for cannabis clubs, particularly in Barcelona, where private consumption and cultivation are permitted.
- United States: Colorado, one of the first states to legalize recreational cannabis, is a key destination with cannabis lounges, farm tours, and events like the Cannabis Cup. Oregon offers farm-to-table cannabis experiences, and Las Vegas is emerging as a hotspot for cannabis tourism.
- Canada: Cities like British Columbia and Toronto offer cannabis tours, lounges, and events, with the Cannabis Expo drawing both industry professionals and enthusiasts.
- India: While cannabis is banned nationwide, the village of Malana in Himachal Pradesh is world-famous for its pure hashish called “the Malana Cream”, attracting global enthusiasts. India also permits bhang, a cannabis-based drink with religious significance in certain states.
- Jamaica: Known for its cultural ties to cannabis, Jamaica is popular for exploring Rastafarian culture, with legal medical cannabis and guided farm tours.
Cannabis tourism contributes to local economies through spending on cannabis, accommodation, and entertainment while creating jobs and encouraging investment. However, challenges such as legal barriers, social stigma, and lack of standardization remain. As legalization spreads, the sector is expected to grow, with eco-friendly tourism and international expansion likely to shape its future.
COVID-19 Impact on the Cannabis Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the cannabis industry, causing shifts in consumer behaviour, supply chains, and retail operations.
Pre-COVID-19
Before the pandemic, the cannabis industry was growing rapidly in regions with legalized markets like Canada and U.S. states such as California. Cannabis was expanding to new areas, and attitudes were becoming more accepting, though some social stigma remained.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, cannabis demand surged as people sought relief from stress and isolation. Cannabis was classified as an essential service, allowing dispensaries to remain open while other stores closed. Popular products like CBD oils, tinctures, and edibles saw increased sales due to their perceived benefits for stress and sleep.
Post-COVID-19
The pandemic caused significant supply chain disruptions, including labour shortages and delays in packaging and lab testing, leading to product shortages, especially in edibles and vape cartridges. To mitigate these issues, the industry shifted toward domestic production, reducing reliance on international shipments.
Retail operations adapted with health protocols like social distancing, masks, and curb side pickup. Virtual consultations and contactless payments. Consumers also became more educated on cannabis strains, dosages, and benefits, with a rise in demand for premium products and those with added health benefits like CBD.
The pandemic accelerated cannabis legalization efforts, with US states like New Jersey and South Dakota legalizing cannabis, while growing public support for legalization drove advocacy for federal action. Cannabis was increasingly recognized as a tool for managing mental health challenges like stress, anxiety, and depression, with products containing CBD and other cannabinoids gaining popularity for their therapeutic potential, but also presents health risks, varying by method, frequency, dosage, age, and health conditions.
Health Risks of Cannabis
Mental Health Risks
High-THC cannabis can trigger or worsen psychosis, anxiety, panic attacks, and depression, especially in vulnerable individuals. Regular use, particularly in adolescence, can impair cognitive function, affecting memory and decision-making.
Physical Health Risks
Smoking cannabis irritates the lungs, causing chronic bronchitis, coughing, and wheezing. It may also increase heart rate and blood pressure, posing risks to those with heart conditions. Around 9% of users develop cannabis use disorder (CUD), and cannabis impairs motor skills, increasing accident risks.
Developmental Risks
Adolescents are at higher risk for substance use disorders and cognitive impairment. Cannabis use during pregnancy can lead to low birth weight and developmental issues, while THC in breast milk affects infant development.
Investments in Cannabis Industry
The global cannabis industry has attracted substantial investments, particularly after the legalization of cannabis in various regions. Many VC firms and PE firms focused on early-stage cannabis startups in areas like cannabis cultivation and product innovation, also invested heavily in larger cannabis companies, looking for growth opportunities as the market matures. As the market matured, institutional investors, hedge funds, and pension funds began entering the space. However, ongoing federal prohibitions in regions like the U.S. limit full investment potential.
Mergers and acquisitions have become common, with large companies acquiring smaller, innovative startups. For instance, in 2021, Tilray merged with Aphria to become the largest cannabis company by revenue. Aurora Cannabis, another Canadian cannabis giant, acquired various smaller companies to enhance its market position, including the purchase of CanniMed in 2018, one of Canada’s first licensed producers.
Companies are also investing in cannabis-related technology, including seed-to-sale tracking, compliance, and AI (Example: Jane, MyHigh and LeafLink). Cannabis real estate is another booming sector, with investors purchasing properties for cultivation and distribution.
Few Leading Cannabis Companies
- Canopy Growth Corporation (TSX: WEED): A major Canadian producer of recreational and medical cannabis, known for partnerships with global brands like Constellation Brands. Currently, the stock is trading at C$2.95 with market capitalisation of ~C$302.254 Mn as of January 28, 2025 (1:56 PM ET).
- Curaleaf (TSX: CURA): A U.S.-based multi-state operator (MSO) with a footprint across many states. Currently, the stock is trading at C$1.87 with market capitalisation of ~C$1.388 Bn as of January 28, 2025 (1:56 PM ET).
- Green Thumb Industries Inc (CSE: GTII): Known for its retail brands like RISE Dispensaries, operating in numerous U.S. states. Currently, the stock is trading at C$10.14 with market capitalisation of ~C$2.145 Bn as of January 28, 2025 (1:58 PM ET).
Cannabis ETFs
- MJ Amplify Alternative Harvest ETF (MJ): Tracks global cannabis-related companies. It is currently trading at $2.08 as of January 28, 2025 (1:59 PM ET).
- Amplify Seymour Cannabis ETF (CNBS): Focuses on cannabis companies involved in cultivation and distribution. It is currently trading at $1.76 as of January 28, 2025 (2:00 PM ET).
- Global X Cannabis ETF (POTX): Provides exposure to a range of cannabis sectors, from cultivation to pharmaceuticals. It is currently trading at $5.15 as of January 28, 2025.
NOTE: Cannabis stocks are volatile, with prices subject to regulatory changes, legal developments, and market sentiment.
Conclusion
The cannabis industry offers strong investment potential, driven by legalization, innovation, and expanding markets. Despite volatility, it presents both risks and rewards, with growth in medical, recreational, and tourism sectors. The COVID-19 pandemic boosted demand, especially in e-commerce, highlighting the industry’s resilience. Legal and social acceptance continues to grow, and as more regions legalize cannabis, the market, particularly in North America and Europe, will continue to expand. However, challenges like the illegal market remain, requiring ongoing regulatory efforts.

