Lithium has emerged as a crucial element in the global transition towards sustainable energy. As the key component in lithium-ion batteries, it powers everything from smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs) and large-scale energy storage systems. With growing demand for clean energy solutions, lithium is playing a pivotal role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and enabling the shift to renewable energy sources. However, its extraction and supply chain challenges raise concerns about sustainability, environmental impact, and future availability. Chemically, lithium (symbol Li, atomic number 3) is a highly reactive, soft, silvery-white alkali metal that does not occur freely in nature. It is primarily sourced from pegmatitic minerals and brine deposits, with its lightweight and conductive properties making it indispensable for modern technology and green innovation.
Lithium batteries play a vital role in modern technology, powering everything from small electronics to large-scale energy storage. They come in two main types: Primary Lithium (non-rechargeable) and Rechargeable Lithium-Ion batteries, which are widely used due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and fast charging capabilities.
Key Applications of Lithium Batteries:
With ongoing advancements in lithium technology, these batteries continue to improve in efficiency, safety, and sustainability, making them indispensable in the transition to a cleaner, more electrified future.
- Consumer Electronics - Lithium-ion batteries are the backbone of modern consumer electronics, powering a wide range of devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, smartwatches, and vaping devices. Their lightweight, high-energy density, and rechargeable nature make them ideal for portable gadgets that require long battery life and quick charging. Unlike traditional batteries, lithium-ion batteries have a low self-discharge rate, allowing devices to retain power even when not in use.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) - The electric vehicle (EV) industry heavily relies on lithium-ion batteries for energy-efficient and sustainable mobility solutions. Companies like Tesla, Nissan, and BMW use these batteries to power their electric cars due to their high performance, fast charging capabilities, and long lifespan. Additionally, e-bikes, scooters, and golf carts benefit from lithium batteries as they offer higher power output, lower maintenance costs, and better overall efficiency compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Renewable Energy Storage - As the world shifts towards solar and wind energy, lithium-ion batteries are playing a critical role in energy storage systems. These batteries store excess energy generated during peak sunlight or wind conditions and release it when energy production is low, ensuring a consistent power supply. Their fast-charging ability and durability make them an ideal solution for off-grid solar systems, residential solar power storage, and large-scale grid stabilization projects.
- Medical Devices - Lithium batteries are widely used in medical devices due to their long lifespan, reliability, and compact size. They are commonly found in pacemakers, defibrillators, insulin pumps, hearing aids, and portable medical monitors. These devices require a stable and long-lasting power source, and lithium batteries provide consistent voltage output and low maintenance requirements, making them essential for critical healthcare applications.
- Emergency Power & UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) - Power outages can be disruptive and even life-threatening in certain situations. Lithium batteries serve as backup power sources in hospitals, data centres, homes, and industrial facilities to ensure uninterrupted power supply. Compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries offer faster charging, longer cycle life, and higher energy efficiency, making them an excellent choice for UPS systems and emergency power backups.
- Security & Surveillance - With the increasing need for remote surveillance and security, lithium-ion batteries provide a reliable power source for cameras, alarm systems, GPS trackers, and monitoring devices. They are particularly useful in off-grid locations or areas with inconsistent power access, such as construction sites, rural properties, military installations, and remote industrial zones. Their low self-discharge rate and long operational lifespan make them the preferred choice for ensuring continuous security monitoring.
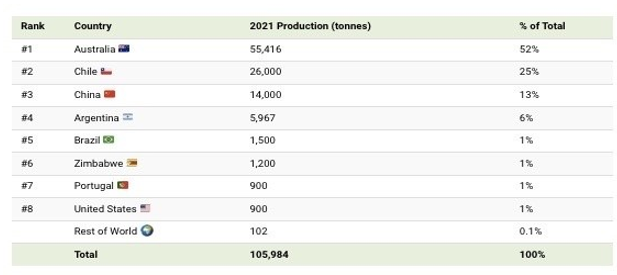
Major Global Producers of Lithium:
As per World Economic Forum, Australia accounts for ~52% of the world's lithium production, primarily extracting the mineral from hard-rock spodumene mines, unlike Chile, where lithium is sourced from brines. China, the third-largest lithium producer, plays a crucial role in the global supply chain. Over the past decade, Chinese firms have invested approximately $5.6 billion in lithium assets across Chile, Canada, and Australia. Additionally, China dominates lithium refining, accounting for 60% of the world’s battery-grade lithium processing (Source: World Economic Forum).
List of Countries that Produce Lithium, Production in Tonnes, 2021:
Source: World Economic Forum
The surge in lithium production is primarily driven by the growing demand for lithium-ion batteries. Lithium is extracted either from brine deposits, which contain lithium-rich groundwater, or through hard rock mining, mainly from spodumene. While Chile holds over half of the world’s lithium reserves, Australia leads in production, with South America specializing in brine extraction and Australia in hard rock mining.
Despite ranking ninth in lithium resources, China’s dominance in refining means its economic conditions significantly impact the global lithium market.
Key Challenges in Lithium-Ion Battery Technology:
- Expanding Production - Meeting the rising demand for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage presents significant challenges. Scaling up production requires massive investments in infrastructure, equipment, and skilled labour. Additionally, manufacturers must balance rapid expansion with quality control and supply chain efficiency, making large-scale production complex.
- Resource Constraints - Lithium-ion batteries depend on limited resources like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, raising concerns about long-term availability and geopolitical risks. As demand grows, securing a stable supply chain becomes increasingly difficult. Ethical and environmental issues linked to resource extraction further emphasize the need for sustainable sourcing and the development of alternative materials.
- Environmental Impact - Despite their role in reducing fossil fuel dependence, lithium-ion batteries have environmental drawbacks. Mining and processing battery materials contribute to habitat destruction, water pollution, and carbon emissions.
The Toxic Footprint of Lithium: Is Green Energy Truly Sustainable?
Lithium and cobalt are essential for renewable energy technologies, including electric vehicles, wind turbines, and solar panels. With the increasing demand for EVs and consumer electronics, the need for these materials is expected to rise significantly by 2030. While their extraction has a lower environmental impact than fossil fuel mining, it still involves energy-intensive processes that contribute to pollution, land degradation, and groundwater contamination.
As per earth.org, Fossil fuel extraction is responsible for around 34 billion tonnes of CO2e emissions annually, whereas cobalt and lithium mining account for approximately 1.5 million and 1.3 million tonnes, respectively. Despite lower emissions, mining these metals still causes habitat destruction, water pollution, and health risks due to toxic metal contamination. Lithium extraction, primarily through brine mining, threatens water sources, while improper battery disposal leads to hazardous metal leaks, underground fires, and respiratory health issues.
As the world transitions to renewable energy, sustainable and responsible sourcing of lithium and cobalt is crucial. Urban planning, economic incentives, and global regulations may be necessary to mitigate environmental damage and promote more efficient extraction methods. Societies have historically adapted to ensure survival and efficiency, and addressing the challenges of lithium and cobalt mining is now more critical than ever.
Few Leading Lithium Producing Companies:
- Albemarle Corporation (NYSE: ALB): Albemarle is an American specialty chemicals manufacturing company based in Charlotte, North Carolina. It operates 3 divisions: lithium, bromine specialties and catalysts. As of 2020, Albemarle was the largest provider of lithium for electric vehicle batteries in the world. Currently, the stock is trading at USD$76.54 with market capitalisation of USD$8.997 Bn as of February 12, 2025.
- Pilbara Minerals (ASX: PLS): Pilbara Minerals is a Perth-based ASX listed company, owning 100% of the world’s largest, independent hard rock lithium operation. Currently, the stock is trading at AUD$2.13 with market capitalisation of AUD$6.82 Bn as of February 12, 2025.
- Q2 Metals Corporation (TSXV: QTWO): A Canadian mineral exploration company focused on unlocking its portfolio of lithium projects in Eeyou Istchee James Bay Region of Quebec, Canada. Currently, the stock is trading at CAD$0.92 with market capitalisation of CAD$125.799 Mn as of February 12, 2025.
How EV and ESS Growth is Driving Lithium Prices:
According to media article that was published on Nasdaq, Demand for lithium-ion batteries is set to continue to grow rapidly in 2025. Benchmark forecasts that EV and ESS-related demand for lithium will both increase by over 30 percent year-on-year in 2025.
Uses of Lithium-Ion Batteries in the world 2015 - 2030
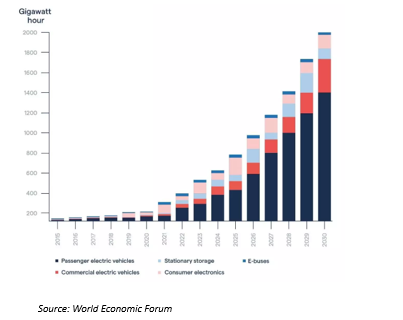
Outlook & Conclusion:
Lithium-ion battery technology has revolutionized energy storage, driving advancements in efficiency, cost reduction, and safety. Despite challenges in scaling production, securing raw materials, and addressing environmental concerns, continuous research and development are unlocking new possibilities. These batteries are now essential for grid energy storage, renewable energy integration, and improving power grid stability.
According to World Economic Forum, the demand for lithium is expected to surge, reaching 1.5 million tonnes of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) by 2025 and over 3 million tonnes by 2030. In comparison, global production stood at just 540,000 tonnes in 2021, meaning supply must triple by 2025 and grow nearly six-fold by 2030.
Despite rapid expansion, bringing new lithium projects online can take 6 to 15 years, leading to a projected supply deficit in the coming years.
Innovations in fast-charging and energy density are helping to overcome key limitations, but fundamental electrochemical constraints may always limit their efficiency in extreme conditions and long-term durability. Nevertheless, with ongoing investment, industry collaboration, and sustainable practices, lithium-ion batteries will remain a cornerstone of clean energy storage, powering the transition toward a more sustainable future.

